Protein Powder: Gainers, Whey Protein, Casein, Soy Protein, Egg Protein, Amino Acids and BCAAs.
Whey protein
Whey protein or whey protein makes up 20% of milk proteins (the other part is casein). This protein is found in the supernatant of yoghurt and is excluded from cheese production due to its poor coagulation capacity. It has several characteristics: high absorption, a high content of branched-chain amino acids (good for muscles) and a faster absorption rate than other proteins.
There are four types of whey:
This is the least successful product. By definition, this product contains about 80% or less protein in the dry extract (specifically, this percentage is lower because the powder contains an average of 5% moisture). The rest consists of carbohydrates (lactose), fat and possibly other residues. It is produced by chemical filtration, which partially distorts the proteins. It is the cheapest and therefore the best selling product that most users turn to.

Whey Concentrate: 100% Whey Protein Professional Scitec Nutrition
This product contains 90% or more protein. There are various types of filtration to remove lactose and unwanted molecules. The two most widely used and well-known methods are ion exchange filtration and cold crossflow microfiltration. The first method uses chemicals (hydrochloric acid, etc.), which denature some of the proteins. The second method is made cold by passing through several filters. It is this method that allows the serum to maintain its amino acid profile unchanged, as well as all of its biological properties. It is also the most expensive method.

Whey Isolate: Zero Carb / Zero Fat IsoGreat by Scitec Nutrition
This protein is completely denatured, but in an interesting way, as you will see below. From the concentrate or isolate, the protein will undergo an enzymatic process called hydrolysis, the purpose of which is to break certain peptide bonds. This constitutes the chemical assimilation of protein. If the process is advanced enough, a completely pre-digested product can be obtained, which will therefore be absorbed very quickly. Most hydrolysates are very bitter, especially because the degree of hydrolysis is high (i.e. quality) due to proline residues that resist hydrolysis. However, there are some costly methods for removing these residues. Thus, we can achieve a degree of hydrolysis of 30%, that is, the product contains about 80% di- and tri-peptides, which is the maximum step until complete hydrolysis, which loses the properties of Peptidpräparate (Peptide). (then the fully hydrolyzed protein becomes a set of free amino acids that is no longer of interest.)
- Bioactive serum or serums with active peptides
This name can hide all types of goods. In theory, they contain serums enriched with peptides with special properties for muscle growth or health (e.g. lactoferrin, immunoglobulins or MicroLactin ® ) or whose protein subfractions have been modified (different proportions of alpha and beta-lactalbumin, more glycomacropeptides, etc.). These products are theoretically the most successful, but currently lack of knowledge leads to some caution.
Proviron
is an active androgen for oral administration. The presence of a methyl group in the C-1 position leads to the special properties of this steroid, which, unlike testosterone and all its derivatives used for androgenic therapy, is not metabolized into estrogen. You can order it here.
Casein
Casein is another component of milk (the remaining 80%). Casein is a protein that has the ability to clot. Thus, during digestion, this process slows down the absorption of proteins, which allows a positive nitrogen balance (anabolism) to be maintained for longer. It can be found in two forms in the appendix:
Like whey concentrate, this is a product that undergoes chemical transformations. This basic and inexpensive formulation allows retailers to sell a product at a higher mark-up due to product quality. This casein is denatured and has lost its spatial configuration (micelles). Thus, it is no longer absorbed gradually as it should. Therefore, it is not very catabolic and its action is short.
This is a kind of casein isolate. The lactose content is low and the protein is well preserved, which allows for a slow diffusion of amino acids and thus plays the desired anti-catabolic role. It is also found in “total milk protein”.

Micellar Casein: Uber Milk Scitec Nutrition
Egg white
Made from egg white, this protein is low in carbohydrates and contains no fat. The egg whites are pasteurized, which ensures the destruction of pathogenic factors, but also allows the protein to be fully digested, since raw egg white can only be digested up to 50% (versus 99% for cooked egg white). It is a quality protein with interesting properties, located between casein and whey: absorption occurs at a moderate rate. However, this protein is no longer popular due to its taste, which is generally less appreciated than whey. However, it remains the protein of choice for those who cannot or do not want to eat milk proteins.
Soy protein
This is a “bump” protein used primarily by vegetarians or vegans. Its amino acid profile is incomplete, it may contain anti-nutritional factors (trypsin inhibitors) that reduce the absorption of dietary proteins (including soy itself), and it contains isoflavones, an antioxidant substance that mimics the effects of estrogen (a female hormone) in the body. Soy protein has an anti-catabolic effect. Its anabolic effect is very weak.
Pea Proteins
Pea proteins are very easy to digest. They are another vegetable alternative to soy. Rich in fiber, their aminogram is a little more interesting. Despite everything, this protein is still underutilized due to its offensive taste to most and its very weak anabolic and anti-catabolic properties.
Amino Acids and BCAA (Branched Chain Amino Acids)
Amino acids are the end product of protein hydrolysis. Usually obtained from bacteria or the hydrolysis of plant proteins, amino acids do not have the biological characteristics that an intact protein (be it a solid food or a powder) would have. Therefore, their role is very meager. They are absorbed relatively quickly, which gives them a slight anabolic property, but which remains very weak for two reasons: first, their origin (hydrolysis of plants) gives them a very uninteresting balance between amino acids (or aminogram), far behind is whey or even soy and and secondly, because of the amount of absorbed product, which is often very low compared to intact protein. To give you an idea, know that delivering the same amount of essential amino acids from a product containing only powdered amino acids is about three to four times more expensive than whey.
So the percentage is very low, doesn’t even exist.
BCAA’s are special. Supplements are very beneficial for several reasons, and the one that interests us the most relates to increasing strength and muscle mass. BCAAs are oxidized during exercise because they are used by muscles as an energy source. The external contribution will compensate for this loss much faster than proteins alone can do (because they do not contain enough). In this way, we optimize muscle recovery and gain. BCAAs also play an important role in the brain, we will look at this in another article.

Super BCAA
Use
As you can see, there is no perfect protein. Each protein will have a different usage time, depending on how you organize your meals and your schedules.
To better illustrate these phenomena, here is the effect of consuming the same amount of different proteins on amino acid levels (blood amino acid levels). The amino acid level shown here accurately reflects what is happening in terms of muscle protein synthesis, that is, in the long term, muscle gain (muscle):
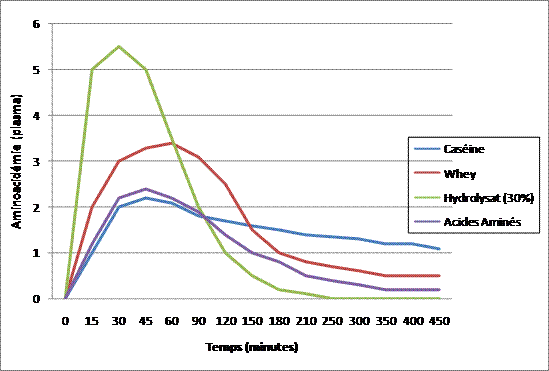
The best choice for your body is the one that allows it to always have what it needs. More specifically, our goal is to maintain a positive nitrogen balance (anabolism) for as long as possible.
With this in mind, we’ll try to spread out protein intake throughout the day, as well as group a significant portion of it when we use it most: around exercise. Indeed, training is a catabolic situation (destruction). And this catabolism occurs immediately, contrary to rumors that it only happens after a certain time (we most often hear “from one hour of training”). But the more time passes, the more it increases. This catabolism is primarily about energy: we use glycogen in the muscles to provide energy for the muscles; but very quickly all the energy systems are involved and your muscle fibers will start to break down during exercise. Later, some of the stress hormones will start to increase, thereby accelerating this catabolism, which will spread throughout the body, which can lead to a collapse of the immune system (which explains why some people get sick the next day or two days after training very intensely). p>
Therefore, our goal is to block this catabolism as much as possible: this is the role of food. By taking protein just before training, it will be in your bloodstream during training, which will limit muscle catabolism (thus promoting post-session anabolism). By taking proteins during exercise (in the form of a hydrolyzate so that they are digested, the digestive system stops functioning at 1/5 of its capacity during exercise, and so that they are immediately available), we can go from a catabolic to an anabolic state, which significantly accelerates recovery, relieve pain and accelerate progression. Finally, by taking protein after exercise, we provide support for muscle anabolism, as our body uses large amounts of protein and energy for at least 24 hours to repair muscle fiber and possibly overcompensate (hypertrophy).
In these three situations, we need fast-digesting proteins, because the faster the protein is digested, the higher the hyperaminoacidemia and the more protein synthesis increases. Therefore, we will choose the serum before and after and the hydrolyzate during. However, whey supplementation may well be replaced by a “solid” protein source such as chicken, tuna, or egg whites. The long-term result will be slightly lower, but it will far outweigh the lack of protein intake.
Also remember what we said about BCAAs: we can therefore further optimize protein intake by boosting them with 10 g of BCAAs during exercise (preferably during or after).
In addition to workouts, protein powder can be used as a meal replacement or as a snack (between meals). In case there are real difficulties in gaining weight, using a weight gainer can be beneficial, but remember that these high-calorie foods gain fat easily and that fat is not muscle and that it does not turn into muscle either!
FAQ
Given the many questions from users of protein powder, I decided to write a small FAQ that I hope most of them will answer.
I’ve heard that eating whey in the morning on an empty stomach stops catabolism and stimulates anabolism, right?
Yes, that’s right. Keep in mind, however, that whey consumed as part of your breakfast will have exactly the same effect. Therefore, it is useless to overload protein with a dose 10 minutes before breakfast, especially if it already contains protein. Supplement sellers are particularly interested in whey.
A friend told me that protein powder is useless, that real food works better.
Indeed, if you manage to eat enough protein in solid form throughout the day, then powders will lose some of their interest. However, whey has certain characteristics, such as the ability to visibly stimulate anabolism over several hours, and whey is only present in small amounts in the diet. Other products such as hydrolysates cannot be substituted for solid products.
I am lactose intolerant, what can I do when it comes to protein powder?
You can choose between egg white or whey isolate and micellar casein. Indeed, the lactose content is low enough not to cause digestive upset, so the digestion of small amounts of lactose is explained in our fiber article.
I have acne when I take protein powder, is it due to lactose? If not, what is the reason?
Lactose intolerance cannot cause acne. You may have allergic reactions and digestive upsets. On the other hand, dairy products that contain it can. This can be explained by several mechanisms: low quality protein may contain hormones and / or milk proteins that will affect some of the growth factors that work in conjunction with DHT (a hormone derived from testosterone)
If I take in more protein, will I have more muscle?
No, because protein is just a building block of muscle. First of all, you need a building signal, that is, training. Once the protein requirement is met, taking more is pointless. The excess will oxidize to provide energy.
Can protein powder be used for cooking?
Yes. Heat treatment is not the same as chemical treatment and does not denature the protein enough to render it useless. For some proteins, cooking even increases digestibility and therefore efficiency.
How to store protein powder?
The protein powder is dehydrated. Therefore, they should be kept away from moisture. Besides, there is no need to store them in any particular place.
Should I take protein powder with water or milk?
Adding milk basically adds two things to the protein: calories (carbohydrates, protein, and possibly lipids) and casein. This will therefore slow down digestion. However, the anti-catabolic role of milk can be very interesting, depending on the timing and your goals. With water, you have a product that can stay in solution in your bag all day long without having to keep it in the refrigerator.
Can protein powder be used while dieting?
Yes. They will help you maintain muscle mass, but they will also help you fight hunger. Indeed, whey has appetite suppressing properties and casein is digested slowly, which also slightly calms the appetite.
Is protein powder harmful to the kidneys?
As with solid foods, protein powder has never had a detrimental effect on kidney function when it is intact. If you already have kidney problems, we recommend that you see your doctor, avoid overusing these supplements, eat a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and monitor your kidneys.
Should I take protein powder on a periodic basis (as a medicine)?
no As explained above, these products are non-doping and have no harmful effects on health. As a solid food, you can use them every day, throughout the year.
Which brand do you recommend?
Brand doesn’t really matter. The only really important thing is the ingredients. Be sure to grab the product that suits your requirements after reading this article.





